In this tutorial, You will learn how to connect to MySQL database from Java program and running SELECT and INSERT queries to retrieve and update data with step by step guide. In order to connect and access MySQL database from Java, you can use JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) API, which is bundled in JDK itself. JDBC allow you to connect to any database e.g. Oracle, SQL Server or MySQL, provided you have the vendor's implementation of JDBC driver interface, which is required to connect database. You can connect to MySQL from Java by using MySQL's Type 4 JDBC driver which is bundled in mysql-connector-java-5.1.23-bin.jar. It's type 4, pure Java driver, which means you don't need any native library or JDBC ODBC bridge, all you need is to put this JAR in your classpath. This JAR contains "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" which is the key for making database connection from Java program to MySQL DB. If this JAR is not present in the classpath, then while running this program you will get java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, so always make sure you have this JAR in the classpath. By the way if you are looking for some good book to master JDBC programming in Java, I suggest you to take a look at Practical Database Programming with Java By Ying Bai. This is one of the relatively latest book on JDBC and cover two of the most popular database SQL Server 2008 and Oracle. This book also teaches you how to work in Netbeans Integrated environment, similar to our example and provides all necessary tools and knowledge to handle database programming in Java. An ideal book for graduate and undergraduate students, as well as database programmers and software engineers.
The JDBC URL for MySQL database starts with "jdbc:mysql" that's the protocol connection is using to connect, followed by host and port where your MySQL database is running. In our case, I am running MySQL server in localhost, which by default listens to port 3306, unless you change it during installation. Next part is "test" which is an empty database which comes with MySQL. I have created a Book table into this database for our example purpose. If you want, you can also create the same table by using following SQL :
and you can use following SQL to populate table with some good books :
When I again ran the Java program after including MySQL JDBC driver in Classpath, I was greeted with following error, because I had included table name also in the JDBC URL String as "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test/book", let's try to run after removing table from JDBC String
Now it ran successful and printed following output :
Total number of books in the table : 2
Which is correct, because our books table only has two books, Effective Java and Java Concurrency in Practice.
By the way, if you have mysql driver during compile time but missed it during run-time, you will get
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. You can follow the solution give here to deal with this error.
This will print following output :
Couple of things to pay attention here. See the rs.getInt(1) method call, well that is to retrieve an integer column, which is "id" in our case. In JDBC, column index begin with 1, so rs.getInt(1) will read first column as Integer. It will throw InvalidColumnIndexException if we provide invalid column index, as many Java developer mistakenly provide "0" for first column i.e. rs.getInt(0). Accessing columns with index is risky, its better to use column name instead of indexes i.e. rs.getInt("id") will return value of id column. It is also one of the JDBC best practices you will learn in my post 10 JDBC best practice for Java developers . Similarly getString() is used to read String or VARCHAR columns. The loop will run until rs.next() return false, when number of rows comes to an end. This query returns 2 rows and that's why the loop runs twice, printing details of two books loaded from MySQL database.
That's all about how to connect to MySQL from Java program. Once you are able to make a successful connection you can run SELECT, INSERT, DELETE or UPDATE query just like you do using MySQL command line client or MySQL GUI. Like connecting to any other database, we have used Connection object to make connection and ResultSet object to get the result of our SQL Query. Just make sure that your MySQL Server is started and running before you connect and mysql-connector-java-5.1.17-bin.jar is in CLASSPATH to avoid nasty ClassNotFoundException.
Once you are comfortable with connecting, retrieving data and inserting data, next step is to learn how to use PreparedStatement in Java to prevent SQL injection. In a production system, you should always use PreparedStatement and bind variables.
If you like this JDBC tutorial and hungry to learn more about connecting and operating database from Java application, you may like following amazing articles too :
Resources :
Connecting to MySQL database using JDBC
In order to connect to MySQL database, you need four things :- JDBC URL (jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test)
- Username ("root")
- Password ("root")
- Database with table to demonstrate query (Book database with few books in test database)
The JDBC URL for MySQL database starts with "jdbc:mysql" that's the protocol connection is using to connect, followed by host and port where your MySQL database is running. In our case, I am running MySQL server in localhost, which by default listens to port 3306, unless you change it during installation. Next part is "test" which is an empty database which comes with MySQL. I have created a Book table into this database for our example purpose. If you want, you can also create the same table by using following SQL :
CREATE TABLE `books` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `author` varchar(50) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
and you can use following SQL to populate table with some good books :
INSERT INTO test.books (id, `name`, author) VALUES (1, 'Effective Java', 'Joshua Bloch'); INSERT INTO test.books (id, `name`, author) VALUES (2, 'Java Concurrency in Practice', 'Brian Goetz');
Java Program to connect MySQL from Java
Now, let's write our Java program to connect to this MySQL database running on localhost. Its important to close database connection, statement and result-set object once you are done with them. It's also important to close them in finally block with their try catch block because their close method can also throw Exception and in that case your program may start leaking those resources, see my post right way to close resources in Java for more details. Alternatively, you can use try-with-resource statement introduced in Java 7 to open and close SQL resources. In fact that's the standard way from JDK 1.7 onward.import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; /** * Simple Java program to connect to MySQL database running on localhost and * running SELECT and INSERT query to retrieve and add data. * @author Javin Paul */ public class JavaToMySQL { // JDBC URL, username and password of MySQL server private static final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"; private static final String user = "root"; private static final String password = "root"; // JDBC variables for opening and managing connection private static Connection con; private static Statement stmt; private static ResultSet rs; public static void main(String args[]) { String query = "select count(*) from books"; try { // opening database connection to MySQL server con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); // getting Statement object to execute query stmt = con.createStatement(); // executing SELECT query rs = stmt.executeQuery(query); while (rs.next()) { int count = rs.getInt(1); System.out.println("Total number of books in the table : " + count); } } catch (SQLException sqlEx) { sqlEx.printStackTrace(); } finally { //close connection ,stmt and resultset here try { con.close(); } catch(SQLException se) { /*can't do anything */ } try { stmt.close(); } catch(SQLException se) { /*can't do anything */ } try { rs.close(); } catch(SQLException se) { /*can't do anything */ } } } }
java.sql.SQLException: No suitable driver found for jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test/book
When I first run this program, I got the error "No suitable driver found for jdbc:mysql", because MySQL driver JAR, mysql-connector-java-5.1.23-bin.jar was not present in classpath.java.sql.SQLException: No suitable driver found for jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test/book at java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(DriverManager.java:689) at java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(DriverManager.java:247) at JavaToMySQL.main(JavaToMySQL.java:29) Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at JavaToMySQL.main(JavaToMySQL.java:46) Java Result: 1
When I again ran the Java program after including MySQL JDBC driver in Classpath, I was greeted with following error, because I had included table name also in the JDBC URL String as "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test/book", let's try to run after removing table from JDBC String
com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.MySQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown database 'test/book' at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.java:62) at sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.java:45) at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Constructor.java:408) at com.mysql.jdbc.Util.handleNewInstance(Util.java:411) at com.mysql.jdbc.Util.getInstance(Util.java:386) at com.mysql.jdbc.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:1053)
Now it ran successful and printed following output :
Total number of books in the table : 2
Which is correct, because our books table only has two books, Effective Java and Java Concurrency in Practice.
By the way, if you have mysql driver during compile time but missed it during run-time, you will get
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. You can follow the solution give here to deal with this error.
How to retrieve data using SELECT Query to MySQL using JDBC
In order to get data from database, you can run SELECT query. In our first example, we have used SELECT query, but we only get the count of records, this time we will retrieve the record itself. most of the program will remain same, except the SQL query and the part which retrieve data from ResultSet object.String query = "select id, name, author from books"; rs = stmt.executeQuery(query); while (rs.next()) { int id = rs.getInt(1); String name = rs.getString(2); String author = rs.getString(3); System.out.printf("id : %d, name: %s, author : %s %n", id, name, author); }
This will print following output :
id : 1, name: Effective Java, author : Joshua Bloch id : 2, name: Java Concurrency in Practice, author : Brian Goetz
Couple of things to pay attention here. See the rs.getInt(1) method call, well that is to retrieve an integer column, which is "id" in our case. In JDBC, column index begin with 1, so rs.getInt(1) will read first column as Integer. It will throw InvalidColumnIndexException if we provide invalid column index, as many Java developer mistakenly provide "0" for first column i.e. rs.getInt(0). Accessing columns with index is risky, its better to use column name instead of indexes i.e. rs.getInt("id") will return value of id column. It is also one of the JDBC best practices you will learn in my post 10 JDBC best practice for Java developers . Similarly getString() is used to read String or VARCHAR columns. The loop will run until rs.next() return false, when number of rows comes to an end. This query returns 2 rows and that's why the loop runs twice, printing details of two books loaded from MySQL database.
How to insert data using INSERT Query to MySQL using JDBC
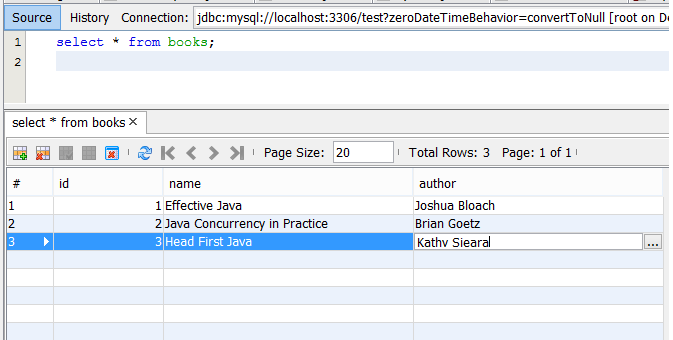
Inserting data is quite similar to retrieving data, just use INSERT query insetead of SELECT query. Also this time, we will use executeUpdate() instead of executeQuery() method. This method is used to run INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE queries and also SQL DDL statements e.g. CREATE, ALER or DROP table that returns nothing, so we don't need ResultSet object. So you must delete all references of ResultSet object from our program, remove executeQuery() and modify SQL Query String as follows :String query = "INSERT INTO test.books (id, name, author) \n" + " VALUES (3, 'Head First Java', 'Kathy Sieara');"; // executing SELECT query stmt.executeUpdate(query);Once you run the program, you can go back and check the database. This time you will see 3 records in your book table, as shown below :
That's all about how to connect to MySQL from Java program. Once you are able to make a successful connection you can run SELECT, INSERT, DELETE or UPDATE query just like you do using MySQL command line client or MySQL GUI. Like connecting to any other database, we have used Connection object to make connection and ResultSet object to get the result of our SQL Query. Just make sure that your MySQL Server is started and running before you connect and mysql-connector-java-5.1.17-bin.jar is in CLASSPATH to avoid nasty ClassNotFoundException.
Once you are comfortable with connecting, retrieving data and inserting data, next step is to learn how to use PreparedStatement in Java to prevent SQL injection. In a production system, you should always use PreparedStatement and bind variables.
If you like this JDBC tutorial and hungry to learn more about connecting and operating database from Java application, you may like following amazing articles too :
- How to connect to Oracle Database from Java Application (learn here)
- What is difference between connected and disconnected RowSet in Java? (answer)
- How to use JDBC connection pool in Spring framework? (solution)
- 5 Simple things to improve performance of Java database applications (tips)
- Difference between java.util.Date and java.sql.Date in Java? (answer)
- How to do INSERT and UPDATE using JDBC Batch statement? (solution)
- 10 JDBC Questions from Java Interviews to answer (questions)
Resources :

No comments:
Post a Comment